Bitcoin’s public narrative is often driven by market speculation and price charts, but the real story in 2025 is unfolding within the protocol itself.
The network is adapting to both internal and external pressures: highly volatile hash power is forcing aggressive adjustments to mining difficulty, while the United States government is making Bitcoin part of its strategic reserve planning.
These developments mark a shift in how Bitcoin operates and how it is treated by state actors, underscoring its evolution as both an economic and political asset.
Network Adjustments Reflect Unstable Mining Conditions
At the core of Bitcoin’s protocol is a simple promise: produce a new block approximately every 10 minutes.
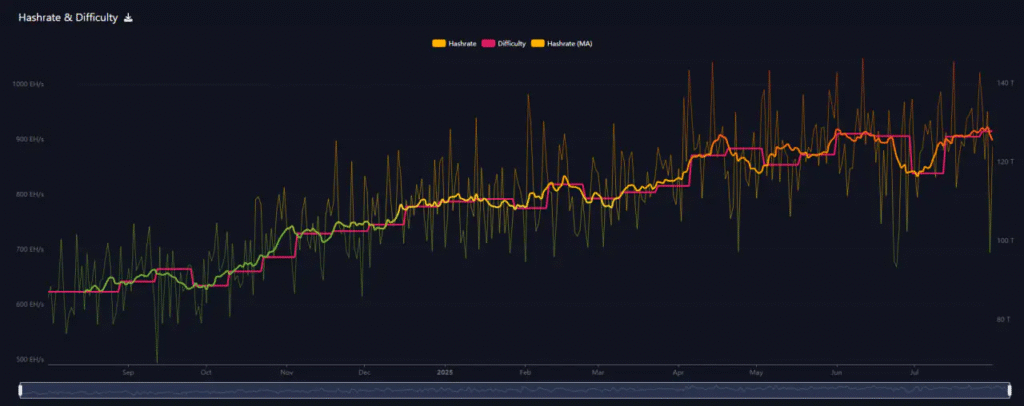
This schedule is upheld through a self-correcting mechanism that adjusts mining difficulty every 2,016 blocks, ensuring the network remains consistent despite fluctuations in computing power. In 2025, however, this adjustment process is being put to the test.
The year has seen a wide swing in Bitcoin’s hash rate, ranging between 700 and 1,000 exahashes per second.
While Bitcoin has always experienced some variation, these current shifts are sharper and more frequent than usual. Day-to-day spikes and drops have outpaced long-term trends, hinting at deeper instability in mining operations.
Large-scale miners, who now represent a significant share of global hash power, appear to be operating with intermittent uptime. Factors such as power supply constraints, maintenance downtime, and shifting energy costs may be contributing to these disruptions.
In response, the network has made seven difficulty recalibrations in just eleven weeks. This level of frequency highlights the extent of ongoing volatility. Most recently, mining difficulty was set at 127.62 trillion after a minor 1.07% increase.
However, the protocol is now preparing for a projected decrease of 4.97% in the next adjustment, one of the sharpest downward moves seen in months.
This shift is not arbitrary. When hash power drops significantly, blocks take longer to mine, slowing down transaction processing. To restore normal timing, the network lowers its difficulty, making it easier for miners to find blocks.
It is a simple yet powerful design, but when hash power itself becomes erratic, the system must overcorrect in both directions.
For miners, this can introduce instability in earnings and long-term planning. For the network, it adds pressure to maintain a balance between consistency and decentralisation.
The underlying cause of this volatility appears to lie in the consolidation of mining resources. As mining becomes increasingly professionalised, a smaller number of operators are responsible for a larger share of network activity.
When these operators experience interruptions, whether technical or economic, the impact is magnified across the entire system.
The protocol can adapt, but the repeated need to do so may reflect deeper concerns about the geographic and operational concentration of Bitcoin mining today.
Despite these challenges, the network continues to function as intended. Blocks are still being produced, and the difficulty adjustment mechanism remains effective.
Yet the pace and scale of recent changes highlight how much pressure the system is under, and how important stability has become to maintaining trust in the network’s long-term security.
Institutional Bitcoin Strategy Enters a New Phase
While Bitcoin’s internal mechanisms adjust to technical pressures, the external political environment is also shifting.
In a rare public confirmation, the Trump administration has announced that the United States government’s Strategic Bitcoin Reserve is now operational.
Although the policy was not heavily detailed in the administration’s most recent digital asset report, Bo Hines, who leads digital asset strategy at the White House, stated clearly that “we have it, it’s been established.”
This confirmation signals a major development in the way governments approach Bitcoin. Estimates suggest that the U.S. currently holds around 198,000 BTC, assets primarily acquired through law enforcement seizures over the past decade. Until now, these holdings were largely viewed as incidental.
That is no longer the case. With the creation of a formal reserve structure, Bitcoin is now being positioned as a sovereign asset, something to be tracked, managed, and potentially deployed as part of national economic strategy.
According to Hines, infrastructure to support this reserve is already being developed. That likely includes custody solutions, internal reporting systems, and potential frameworks for leveraging Bitcoin within broader fiscal or geopolitical contexts.
The move is not just administrative, it places Bitcoin in the same category as traditional reserve assets, even if not officially declared as such.
At the same time, the U.S. regulatory environment for digital assets is undergoing rapid transformation. SEC Chairman Paul Atkins recently introduced reforms aimed at simplifying the classification of cryptocurrencies and making tokenised securities more accessible.
These changes are intended to reduce ambiguity and provide a clearer foundation for digital asset projects to operate within the law.
Although Bitcoin itself is not subject to the same classification questions as other tokens, these reforms help legitimise the broader ecosystem in which Bitcoin functions.
The administration is also pushing for stronger collaboration between the SEC and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission. This kind of regulatory alignment is meant to streamline oversight and reduce the current fragmentation of rules across different agencies.
The implications for Bitcoin are significant, which is a more coordinated regulatory structure could open the door to deeper institutional participation, stronger infrastructure, and more predictable legal treatment in the long term.
These policy moves arrive alongside notable on-chain activity. In recent months, Bitcoin whales have accumulated nearly 1% of the total supply, a substantial shift in ownership concentration. In just 48 hours, 30,000 BTC were added to long-term wallets, even as some early holders, including a Satoshi-era whale, began to liquidate.
While this tug-of-war between old and new participants continues, the broader picture is one of confidence. Institutional and government actors are no longer observing from the sidelines. They are actively entering the system and shaping its next chapter.
New technological projects are also reflecting this shift. Bitcoin Hyper, a Bitcoin-native Layer 2 solution powered by the Solana Virtual Machine, recently surpassed $6 million in its public presale.
The platform aims to bring scalable smart contracts, decentralised applications, and asset creation to Bitcoin, all while preserving its core principles.
Although still in its early stages, Bitcoin Hyper represents the growing interest in extending the Bitcoin network’s functionality beyond its original purpose, aligning with the broader trend of formal adoption and experimentation.
Conclusion
Bitcoin’s position in 2025 is defined not by price movements, but by structural change. Internally, the protocol is working harder than ever to keep up with volatile mining conditions, revealing both its resilience and the strain placed on decentralised infrastructure.
Externally, governments and institutions are beginning to treat Bitcoin not as an anomaly, but as an asset worth integrating into national strategy.
The United States’ decision to formalise its Bitcoin holdings and develop a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve adds a new layer of legitimacy.
Combined with ongoing regulatory reform and increased institutional participation, Bitcoin is entering a phase where operational stability and political recognition matter more than hype.
These changes are not cosmetic. They reshape the incentives, participants, and infrastructure that define the network. As Bitcoin continues to evolve, its future will be shaped not only by code and computation, but also by the growing network of human decisions now forming around it.

