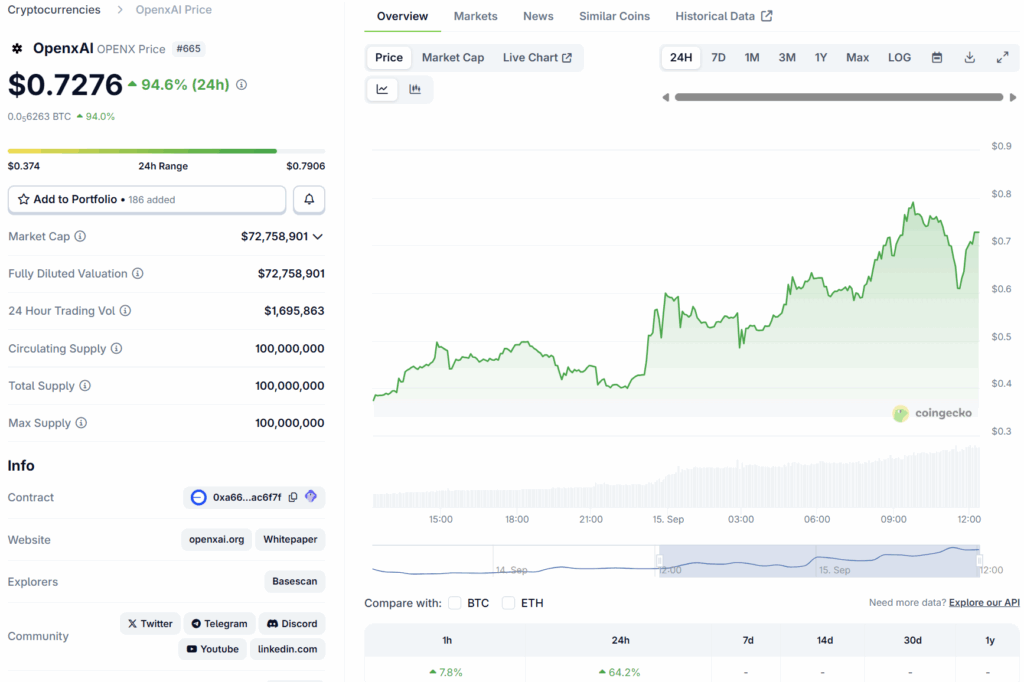
The OpenxAI token has stunned the market with a 100% surge in value in under 24 hours, bringing fresh attention to a project positioning itself at the centre of decentralised artificial intelligence.
Traders, developers, and institutions are suddenly watching closely. But before rushing to buy into the hype, it is worth examining what OpenxAI actually is, how it works, and what role its token plays in this ecosystem.
This article takes a deep dive into the protocol’s technology, vision, and economy to help readers understand the foundation behind the price movement.
What is OpenxAI?
OpenxAI describes itself as the world’s first peer-to-peer permissionless AI protocol. In simple terms, it aims to do for intelligence what Bitcoin did for money.

Instead of AI models being confined to large corporate data centres and guarded by licensing barriers, OpenxAI allows anyone, anywhere, to launch, own, and monetise artificial intelligence directly on-chain. It presents itself as borderless, free from banks, corporations, or governments.
The project’s vision is to create a global economy where intelligence flows as freely as digital money. By eliminating centralised gatekeepers, it offers the opportunity for developers, researchers, and enterprises to access infrastructure, datasets, and AI services on equal terms.
Its mission aligns with an ambition to remove obstacles created by corporate capture, geopolitical restrictions, and prohibitive pricing of cloud services.
What makes OpenxAI particularly attractive is its promise of efficiency. By running entirely on decentralised infrastructure, it claims to cut GPU costs by up to 80% compared to providers such as AWS or Google.
This is achieved through a network of independent operators contributing compute capacity, creating a global alternative that is censorship-resistant, transparent, and scalable.
The network is already supported by contributors with experience from ecosystems such as Solana, Fantom, and Binance, which lends further credibility to its design and goals.
The promise of permissionless access, cost efficiency, and sovereignty over intelligence makes OpenxAI an ambitious attempt to reshape the economics of artificial intelligence.
The appeal goes beyond speculation; it taps into growing frustration with the concentration of AI power in the hands of a few.
How Does the Infrastructure Work?
The foundation of OpenxAI is a layered architecture that converts raw computing resources into programmable, liquid assets. At its heart is the Xnode system, a modular framework that abstracts complex AI tasks into containerised microservices.
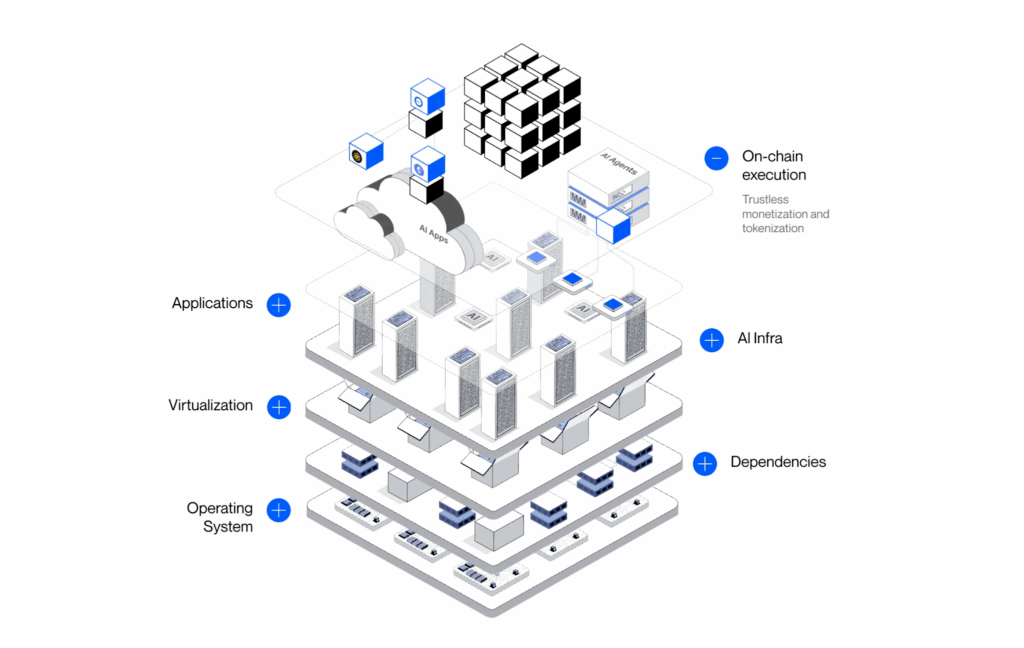
This approach ensures resilience, scalability, and seamless integration. Each Xnode can be deployed on bare metal or cloud infrastructure, and is managed through XnodeOS, a secure operating system based on NixOS.
The network operates across several functional layers. The Resource and Provider Layer is where independent operators register hardware resources such as GPUs, CPUs, and storage.
These are advertised to the network and constantly monitored for health and availability. On top of this, the Tokenisation and Metering Layer converts compute into tradable credits known as tGPU or tCPU.
These credits are minted against verified capacity and burned upon use, creating a transparent system for usage and settlement.
Jobs are assigned to Xnodes by an orchestration engine that matches tasks with available resources based on latency, pricing, and policy. This ensures cost effectiveness and reliability while enabling real-time discovery of compute prices globally.
Once workloads are matched, they are executed by the X Engine runtime inside reproducible containers. This allows for training, inference, and deployment of multi-model applications wallet-to-wallet without any central server.
Security is a critical component. Authentication is handled through Web3 wallets, ensuring decentralised access control, while immutable configurations provide resistance against tampering.
Governance and trust mechanisms such as staking and slashing are built into the protocol, ensuring that operators provide honest capacity and cannot capture the network.
All of this is coordinated under the governance of the OpenxAI DAO, where token holders make decisions on upgrades, funding, and incentives.
This infrastructure transforms AI from a centralised service into a programmable, distributed economy. It ensures that compute resources become not only functional but financial primitives in their own right.
What Can It Be Used For?
The applications of OpenxAI extend far beyond hosting models. The protocol is designed to support a broad marketplace of intelligence where developers, businesses, and individuals can interact in a peer-to-peer environment.
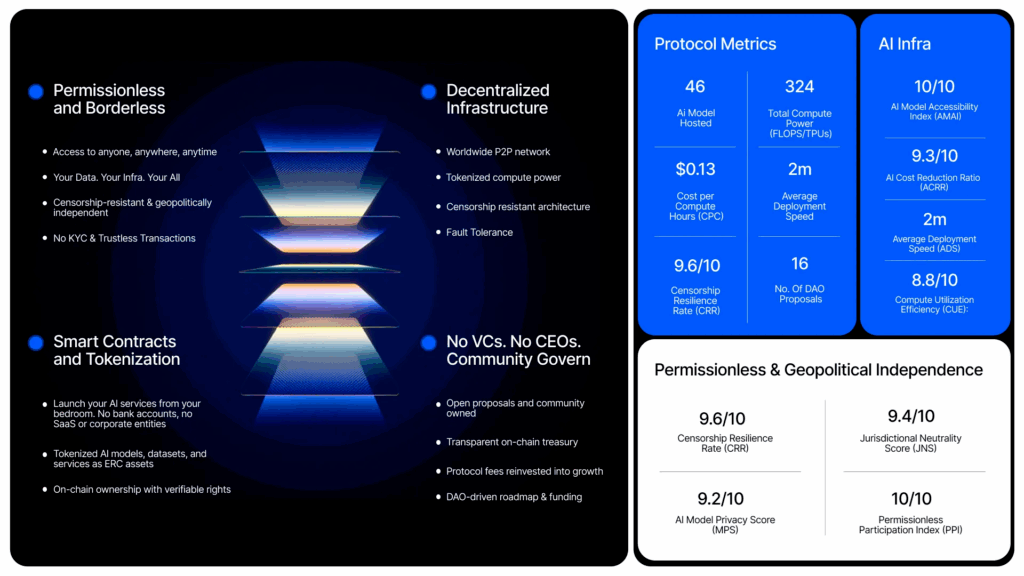
At the most basic level, it allows anyone to deploy AI models quickly through OpenxAI Studio, a no-code drag-and-drop platform. Models can be selected from an app store, deployed onto bare metal servers, and interacted with via interfaces such as Ollama.
This lowers the barrier for developers who may not have extensive infrastructure knowledge, enabling rapid experimentation and scaling.
The GPU marketplace further expands accessibility. Instead of relying on centralised providers, developers can browse a global catalogue of GPU machines, filter by price or region, and deploy workloads at competitive rates. This creates an efficient allocation of idle capacity while giving providers a new revenue stream.
For creators, the protocol enables monetisation of models, datasets, and agents. These assets can be tokenised, wrapped as NFTs, and sold or licensed in the marketplace.
Smart contracts ensure that royalties and subscription payments flow directly to creators. This establishes provenance for AI assets and rewards contributions in a transparent way.
The protocol also opens new possibilities for financial innovation. With compute tokenised into fungible credits, it can be traded, staked for yield, or used as collateral in decentralised finance systems.
This “ComputeFi” economy turns GPUs and CPUs into programmable capital, unlocking liquidity for what was previously an illiquid resource.
The range of applications is vast: from research projects accessing affordable compute, to enterprises building large-scale copilots without central licensing, to students experimenting with advanced models.
By combining peer-to-peer execution, tokenisation, and on-chain settlement, OpenxAI creates an open marketplace for intelligence where anyone can participate.
The OPENX Token
At the core of the network’s economy is the OPENX token, which serves as the unit of settlement, governance, and incentives. The total supply is capped at 100 million tokens, with the circulating supply initially limited to a small percentage to encourage sustainable growth.
OPENX is used to pay for compute workloads across Xnodes, either directly or through credits such as tGPU and tCPU. These credits are minted against node capacity and burned upon use, creating demand-driven scarcity for the token.
Marketplace fees, licensing payments, and subscription revenues are also denominated in OPENX, which ensures continuous utility across the ecosystem.
Holders of the token are not passive. They can stake OPENX to secure the network, support node operators, and earn rewards tied to actual demand rather than inflationary emissions.
Governance is structured around a burn-to-vote mechanism, where holders commit tokens to signal long-term alignment with the protocol. This provides influence over treasury allocations, upgrades, and ecosystem initiatives.
The design ensures that value flows back to those who contribute. Node operators earn tokens for providing reliable capacity, developers earn royalties when their models are used, and token holders receive staking rewards.
The DAO treasury also collects protocol fees, which are reinvested into grants, community programmes, and ecosystem growth.
This creates an economic flywheel: more adoption leads to more demand for compute, which burns more tokens, reducing supply and increasing value.
In turn, a higher value attracts more operators and developers, which expands network capacity and applications. The cycle reinforces itself, creating long-term sustainability.
Conclusion
The recent 100% surge in OpenxAI’s token has captured market attention, but its real significance lies in the technology and vision behind it.
By transforming compute into liquid capital, enabling peer-to-peer AI deployment, and rewarding creators through on-chain commerce, OpenxAI positions itself as a serious contender in decentralised infrastructure.
While volatility will come and go, the underlying model represents a step towards an open economy of intelligence.
For those considering participation, the deeper value lies not in short-term speculation but in the long-term potential of a network designed to make AI accessible, transparent, and truly permissionless.